Chemistry

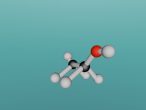
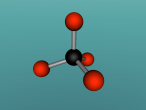
Ethanol Molecule
Ethanol is a molecule containing a mere 9 atoms of which there are 3 different atoms and has been known to human long prior to the advent of modern chemistry.
- 2 comments
- Read more
- 6623 reads
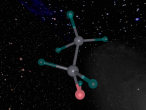
The Methane Molecule - E-Yong Lee
Introduction
Methane. (Science: chemistry) A light, colourless, hydrocarbon which is toxic by both inhalation and skin exposure. Also infamously known for being the main substance found in flatulence (the bodily function is actually made up of 59% nitrogen and 21% hydrogen, just saying.) Nevertheless, this blog will explore the structure, composition and characteristics of Methane. Methane contains carbon and hydrogen in the ratio of 1:4 respectively. Since methane is both a powerful greenhouse gas and the simplest and most effective hydrocarbon. It is the main gas found in natural gas piped for use in homes, used to generate electricity and is even used as rocket fuel.
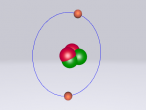
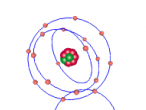
Nitrogen Atom
Nitrogen has an atomic number of seven making it the seventh element on the periodic table. A component of protein, nitrogen is a definite necessity to life but in large quantities it can be harmful. It is "the fifth most abundant element in the universe" and is found present in organic materials, foods, fertilisers, explosives and poisons. On Earth nitrogen can be found almost anywhere as it makes up 78% of the Earth's air. (Blaszczak-boxe, 2014) The nitrogen molecules are found mostly in the air however they can are also found in water and soil as nitrates and nitrites which are part of the nitrogen cycle. Natural nitrate and nitrite have been modified by humans who have emitted excess nitrogen, increasing the original proportions. This is due to the manufacturing of nitrate-containing manures by larger industries. The majority of consequences are mostly negative, for example higher levels of nitrate in drinking water causes health risks. (Lenntech, 2016).

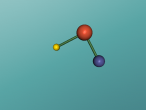
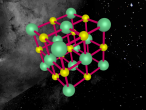
Sodium Chloride Molecule
Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter, fundamental and key to the formation of everything that exists around us. They make up the air, our bodies and even the very screen that you are staring at right now. Each atom has its own unique atomic structure along with its different characteristics.
These atoms join together into groups to form molecules of either elements or compounds. Elements can only consist of the same type of atoms that cannot be broken down into simpler substances, whereas compounds are made of two or more elements that are chemically bound together. An example of an important molecule in everyday life is Sodium Chloride or commonly known as salt.