Chemistry
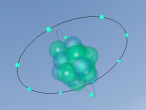
Silicon Atom
My partner and I have decided to research and create a 3D model of the element silicon. Silicon is an element present in the periodic table, possessing the atomic number of 14. Its atomic mass number is 28.085 and its state at room temperature is solid. It is known to be the "seventh most abundant element in the universe and the second most abundant element in the Earth's crust" (Gagnon, S., n.d.). Silicon has various uses including improving the strength of aluminium alloys, helping the operation of electronic products in the form of chips and being the main material that solar panels are made of (SIMCOA, n.d.). Most silicon on earth is found in the crust as sand, quartz and rock crystals among others. The discovery of silicon is credited to Swedish chemist Jöns Jacob Berzelius in 1824. He heated chips of potassium in a silica container then washed away the byproducts.

Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is a non-flammable colourless liquid with a sharp odour (National Centre for Biotechnology Information, 2016).
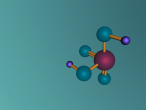
Sulphuric Acid
Sulphuric Acid
ETHANE MOLECULE
Ethane
Ethane, otherwise known as C2H6, is an organic compound which is a colourless, liquefied gas. It provides many uses including those from the industrial and a consumer point of view. Ethane is used in fuel, fuel additives, ion exchange systems, paint additives, pigments, plasticizers, building/construction materials, fabric products, textile products, leather products, food packaging and much more.
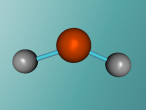
H2O Molecule
Imagine you are sitting with your feet in a pool (filled with liquid water), watching the steam (gaseous water) rise from the spa nearby as you sip a drink from your glass filled with ice cubes (solidified water). Not many other chemical substances can exist in all three states of matter within the same temperature range. In fact, water it is the only substance which naturally occurs in all types. This is why H2O (commonly called water) is one of the most interesting chemical compounds in the universe, as well as being essential for life! (We have never found any organism that doesn't contain H2O) Apart from being the most abundant compound on the Earth's surface, it has many other unique properties such as it's polar covalent bonds.
Ammonia Molecule
Ammonia (NH3) is a molecule which consists of three hydrogen atoms and a nitrogen atom bonded together. It is a colourless, odorous, alkaline gas which is produced when organic materials decompose. This molecule is essential to many plants and animals, as a source of nitrogen. Additionally, bacteria within the intestines can produce the substance. Ammonia has many uses, though it is mostly used in fertilisers and cleaning products.