Chemistry

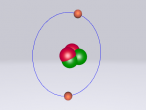
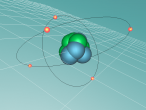
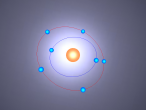
Carbon Atom
All around us, everything we see is made up of incredibly small pieces of matter called atoms. These atoms, though incredibly small, are the building blocks for everything on earth and the rest of the universe, from buildings to people to even the stars. One particularly interesting atom that we will be discussing in this blog is Carbon. Carbon, though relatively small and simple compared to most other atoms, has played a massive role in the history of the earth, most notably being an essential part in all life known to humans.
Positioned at 6th on the periodic table, carbon is the sixth most common element in the universe, and fifteenth most common on earth. This is largely due to its relatively basic structure, and in its most common state, Carbon 12, it only has 6 protons, 6 neutrons and 6 electrons, with the electrons arranged into an inner shell of 2 and an outer shell of 4. It is considered fairly light, with an atomic weight of 12 amu, and is generally found as a solid on earth, with a melting point of 3550°C and boiling point of 3825°C. Carbon has fifteen isotopes, from Carbon 8-22, but Carbon 12 and 13 is considered stable. The isotope Carbon 14 is often used in Carbon dating on bones and pieces of plants to determine their date.
Carbon had been discovered by humans many thousands of years ago, and was first used in the form of charcoal at least 28 thousand years ago in rock art and cave paintings. At least 3000 years ago, diamonds, another allotrope of Carbon, were already being used as religious items and to engrave tools with, though their popularity later soared when they were used in jewellery. In 1772, Antoine Lavoisier first proved the existence of carbon, when after burning both diamonds and charcoal, he discovered they both released the same amount of carbon dioxide. Only 7 years later, Carl Wilhelm Scheele discovered graphite was also a form of carbon, and it is now used widely in a variety of areas, particularly in pencils. Though it had also been used for thousands of years in fires, coal, another form of carbon, also became incredibly important around this time and was essential to sparking the industrial revolution, and around 80% of our energy still comes from Carbon-based fossil fuels such as coal, oil and natural gasses. In modern times, Carbon in the form of various allotropes is still used in surprisingly similar ways to earlier times in history, though various other new uses for the element have been found throughout the last few thousands of years.
Another important quality of carbon is its valence electrons, which gives the atoms the ability to effectively bond with both more carbon atoms and a wide variety of other atoms, allowing for complex and diverse chemical bonds, structures and molecules that are essential to all life forms on earth. Without this unique property, as well as its small size, light weight and abundance on earth, life would be unable to exist, and the world would still be a barren wasteland, devoid of any living creature. This is by far one of the most important qualities of carbon, and another reason why it is such an important and special element.
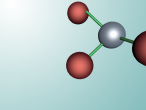
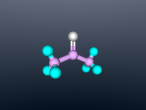
Aluminium Chloride
Compounds are substances which are formed when two or more chemical elements are chemically bonded together. Compounds are found everywhere, from the water (H2O) which we drink, to the aluminium chloride we use as a deodorant. They consist of various atoms arranged in a specific structure, called molecules. Compounds are formed through two types of chemical bonding, covalent and ionic bonding. A covalent bond is formed when electrons are shared between atoms, whereas ionic bonds are formed through the attraction of oppositely (positive charge and negative charge) charged ions.
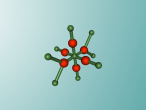
Calcium Chloride
Introduction
This blog will detail the composition, structure and characteristics of calcium chloride and includes
Boron Atom (By Melody Suen)
At the QUT workshop, I learnt how to use VRMath 2.0 to program, create 3D molecules/atoms and how to write a blog. With my partner Hana, we created a 3D model of a boron atom. In this blog post, I will explain the composition, structure and characteristics of boron, as well as the programming used.
Acetone Blog
My name is Michaela Cheong and I am a student at Brisbane State High School. In our current unit of science, we are learning about chemistry, specifically the structure and characteristics of atoms (building blocks which make up everything) and compounds (consist of two or more atoms which are chemically bonded). In this blog, I will show you a 3D model of a molecule of acetone along with a discussion of it’s molecular structure, uses and properties.
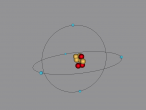
Nitrogen Atom
It is an element that is an essential to all life on Earth, yet in its purest form it can suffocate living organisms. Nitrogen is one of the most important elements on Earth – it can be found in all living systems and makes up around 78% of the Earth’s atmosphere. It is a constituent of protein and nucleic acids. In its gaseous form, nitrogen is colourless, odourless and generally considered inert. In its liquid form nitrogen is also colourless and odourless, and resembles water. Nitrogen was first recognised in 1772 by number of scientists; Carl Wilhelm Scheele, Daniel Rutherford, Henry Cavendish and Joseph Priestley, who all found that air was composed of three different gases, oxygen, carbon dioxide and another gas which they dubbed ‘foul air’ (nitrogen). Nitrogen was first recognised as an element by Antoine Laurent Lavoiser in 1786, and named nitrogen in 1790 by Antoine Laurent Lavoiser. Today, nitrogen is used in food preservation, explosives, and aids medical research.