Science
The Methane Molecule - E-Yong Lee
Introduction
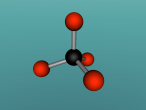
Methane. (Science: chemistry) A light, colourless, hydrocarbon which is toxic by both inhalation and skin exposure. Also infamously known for being the main substance found in flatulence (the bodily function is actually made up of 59% nitrogen and 21% hydrogen, just saying.) Nevertheless, this blog will explore the structure, composition and characteristics of Methane. Methane contains carbon and hydrogen in the ratio of 1:4 respectively. Since methane is both a powerful greenhouse gas and the simplest and most effective hydrocarbon. It is the main gas found in natural gas piped for use in homes, used to generate electricity and is even used as rocket fuel.
Nitrogen Atom
Nitrogen has an atomic number of seven making it the seventh element on the periodic table. A component of protein, nitrogen is a definite necessity to life but in large quantities it can be harmful. It is "the fifth most abundant element in the universe" and is found present in organic materials, foods, fertilisers, explosives and poisons. On Earth nitrogen can be found almost anywhere as it makes up 78% of the Earth's air. (Blaszczak-boxe, 2014) The nitrogen molecules are found mostly in the air however they can are also found in water and soil as nitrates and nitrites which are part of the nitrogen cycle. Natural nitrate and nitrite have been modified by humans who have emitted excess nitrogen, increasing the original proportions. This is due to the manufacturing of nitrate-containing manures by larger industries. The majority of consequences are mostly negative, for example higher levels of nitrate in drinking water causes health risks. (Lenntech, 2016).

Sodium Chloride Molecule
Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter, fundamental and key to the formation of everything that exists around us. They make up the air, our bodies and even the very screen that you are staring at right now. Each atom has its own unique atomic structure along with its different characteristics.
These atoms join together into groups to form molecules of either elements or compounds. Elements can only consist of the same type of atoms that cannot be broken down into simpler substances, whereas compounds are made of two or more elements that are chemically bound together. An example of an important molecule in everyday life is Sodium Chloride or commonly known as salt.

Sodium Fluoride
Sodium fluoride is a molecule which is made up of sodium (Na) and fluoride (F) with a ration of 1:1. The blog presented will be describing and explaining the composition, structure and characteristics of this molecule. It's most common use, as afore mentioned is in toothpaste, where it strengthens the teeth, and makes them more resistant to decay caused by acidic substances and bacteria. Sodium toxic is highly toxic and can be lethal to humans if ingested in large quantities. This makes it effective for rat poisons and insecticides. It also is used as a cleaning agent.
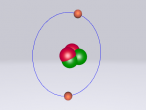
Ethanol Molecule
VR MATHS 2.0 BLOG-Yerong Yang
Atoms are the fundamental units and building blocks of matter. The periodic table lists the currently discovered pure elements that are used to form other substances. Along with these stable elements, there are a variety of other atoms and molecule types that are built and bonded together to form new compounds. The substance ethanol consists of molecules that a joint to form this chemical drug. Ethanol molecules are formed from different types of elements and share different bonds to form their molecular state. This blog displays the completed 3D theoretical model of the chlorine atom based on the current information that's up to date on this known molecule. The blog will explore the properties and different aspects of ethanol as well as the development of the model on the program VRmaths 2.0.
Sodium Flouride 3D Model
3D Model of Fluorine Atom
3D Models of Atom Blog – Fluorine
Introduction:
The topic of this blog is going to be about an atom i.e. fluorine. Using a program called VRMath2.0, my group created a 3D model of fluorine which included the nucleus of the atom and its outer shells. This blog will include the following components: a 3D model of the atom Fluorine, a description on the composition, structure and characteristics of Fluorine, questions that I wish to investigate further and the difficulties that I experienced throughout the programming.
Fluorine is a chemical element represented by the symbol ‘F’ and has an atomic number of 9. It is classified as a non-metal and is the first element in the family of halogen gases. Given that it is the top element in the Halogen Group, it is the most electronegative element and therefore is very reactive. (Feldman, R. & Marsden, S., 2015) There are a few common usage of Fluorine and this element can be found in a variety of items and objects including rocket fuel, refrigeration fluids and toothpaste (helps to prevent tooth decay). (Chem4Kids, 2016)