Science

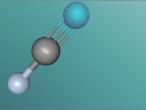
Hydrogen cyanide
Hydrogen cyanide, otherwise known as prussic acid is lethal to humans when a large enough quantity is ingested (approximately 150mg/m-3) and has a LD50 2857mg/kg of body weight. With a boiling point of 26°C and a melting point of 12-14°C, hydrogen cyanide is mostly found in its gaseous or liquid state, where it is most fatal as it is a systemic chemical asphyxiant where when the cyanide ion cyanide ion halts cellular respiration by acting as a non-competitive inhibitor for an enzyme in the mitochondria called cytochrome oxidase, halting ATP production in the mitochondria. However, hydrogen cyanide is a precursor to products from polymers to pharmaceuticals as it is then in small enough doses that there is no physical affect to the human body.