Brisbane State High School
In this group, Year 9 students will be creating 3D atomic models and blogging about the characteristics, structure and composition of atoms and molecules. Together we are learning and sharing our knowledge construction about atoms and molecules.
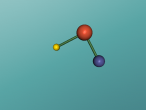
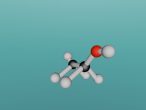
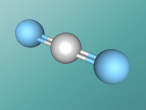
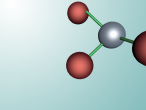
For example, below is a model of a helium atom and a water molecule.
Please download the attached Aspire Science Workshop Handbook.pdf at the end of this group page. Before the workshop at QUT, you should have followed the handbook to at least section 3.5. In addition to this handbook, you may try:
- The VRMath2 Wiki has some tutorials about how to edit and publish.
- Students can also post in the VRMath2 forum for technical support.
The Aspire Science VRMath2 Workshop @ QUT
This Workshop will be held on Tuesday 19th July from 9 am to 2:30 pm, at S Block, Creative Inquiry Space (S307/308), QUT Kelvin Grove Campus. The building S Block is right next to the Kelvin Grove bus station of Inner Northern Busway (See attached campus map for details). It is suggested that you should arrive between 8:30 am to 9:00 am for setting up your groups and wifi access. The Workshop will begin promptly at 9 am. If you are taking public transport, bus will be the best choice. Please check on TransLink website to find out your bus routes.
If you are being dropped off by private cars, the best place to drop off will be near the intersection between Victoria Park Road and Blamey Street (see the attache Campus Map for details). Then you can walk up Ring Road to S Block.
NOTE: Due to construction, the Ring Road may be closed so try not to drop off at Ring Road.
Latest Group Blogs
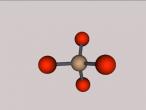
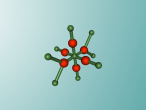
Aluminium Chloride Molecule
Atoms are the smallest particle of an element and are the basic building blocks of all matter. Atoms are composed of a nucleus which contain positively charged particles called protons and no charged particles called neutrons. Surrounding the nucleus are negatively charged electrons arranged in shells. These electrons exist in a cloud around the nucleus. When two electron clouds of different atoms interact, they bind together to form a molecule. An example of a molecular compound (a molecule that contains atleast two or more different elements) is Aluminium Chloride (AlCl2).

Carbon Atom
Aluminium Chloride
Calcium Chloride
This blog will detail the composition, structure and characteristics of calcium chloride and includes
- 62544 reads