Brisbane State High School
In this group, Year 9 students will be creating 3D atomic models and blogging about the characteristics, structure and composition of atoms and molecules. Together we are learning and sharing our knowledge construction about atoms and molecules.
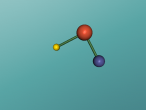
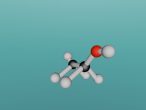
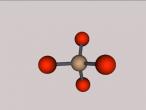
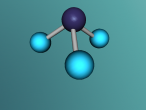
For example, below is a model of a helium atom and a water molecule.
Please download the attached Aspire Science Workshop Handbook.pdf at the end of this group page. Before the workshop at QUT, you should have followed the handbook to at least section 3.5. In addition to this handbook, you may try:
- The VRMath2 Wiki has some tutorials about how to edit and publish.
- Students can also post in the VRMath2 forum for technical support.
The Aspire Science VRMath2 Workshop @ QUT
This Workshop will be held on Tuesday 19th July from 9 am to 2:30 pm, at S Block, Creative Inquiry Space (S307/308), QUT Kelvin Grove Campus. The building S Block is right next to the Kelvin Grove bus station of Inner Northern Busway (See attached campus map for details). It is suggested that you should arrive between 8:30 am to 9:00 am for setting up your groups and wifi access. The Workshop will begin promptly at 9 am. If you are taking public transport, bus will be the best choice. Please check on TransLink website to find out your bus routes.
If you are being dropped off by private cars, the best place to drop off will be near the intersection between Victoria Park Road and Blamey Street (see the attache Campus Map for details). Then you can walk up Ring Road to S Block.
NOTE: Due to construction, the Ring Road may be closed so try not to drop off at Ring Road.
Latest Group Blogs
Ammonia molecule
Atoms are the basic building blocks of all matter. This means that everything around you, including yourself, are made up of atoms. However, what happens when these atoms join together chemically? Well, they form compounds called molecules. Molecules are composed of chemically-bonded atoms and they have a neutral charge unlike an ion, meaning that they have the same amount of protons and neutrons total. Atoms can never be created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction, so they can only break off and form new molecules. Ammonia is a type of molecule and is composed of of one nitrogen atom and three hydrogen molecules, with the chemical equation being NH3. It is described as a colourless, pungent gas. The major use of ammonia is in fertilisers because they are a great source of nitrogen in fertilisers (nitrogen enhances leaf growth). The chief commercial method of producing ammonia is by the Haber-Bosch process, involving the direct reaction of elemental hydrogen and elemental nitrogen. Its boiling point is -33.35oC and its freezing point is -77.7oC.
Aluminium Blog
My partner and I decided to investigate the atom ‘Aluminium’ and proceeded to research about. Through our research, we found that aluminium is a chemical element in the boron group with the symbol Al and atomic number of 13. It is a silvery-white, light-weight metal that is soft and malleable (Royal Society of Chemistry). Aluminium is the third most plentiful element in the earth’s crust, comprising 8% of the planet’s soil and rocks (Lenntech). In nature, aluminium is found only in chemical compounds with other elements such as sulphur, silicon and oxygen, however pure metallic aluminium can be economically produced from aluminium oxide ore or extracted from bauxite by electrolysis (Australian Government – Geoscience Australia). There are several uses of this metal including packaging materials such as foil and cans as well as the construction of transport i.e. automobiles, aircraft fuselages etc. (HowItsMade).

FINAL Methane Blog by Anna Lei (ASC092A)
The compound methane has the chemical formula of CH4. Methane is the simplest hydrocarbon of the paraffin series and a potent greenhouse gas, as well as being a large component of natural gas. The major human-associated source of methane is the production/combustion of coal (Britannica, 2016). In nature, methane is the product of anaerobic bacterial decomposition and certain human/animal activities (7% methane in flatulence). It can be found in wetlands, termites, landfills, volcanoes and oceans. The abundance of methane makes it a widely used fuel for heat and light (energy) production (ARM, 2016). In this blog, the details of methane will be uncovered.
- 2 comments
- Read more
- 4167 reads
- 62597 reads