Carbon Dioxide Molecule
Carbon dioxide, which has the molecular formula CO2, is a chemical compound discovered by Joseph Black, a Scottish scientist, in the 1750s. It is a colourless, odourless gas produced by respiration and combustion.
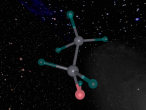
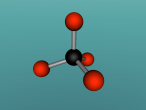
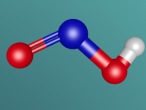
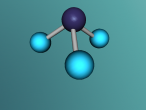
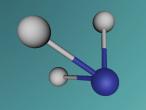
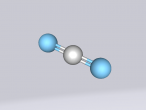
Below is my three dimensional model of a carbon dioxide molecule (the white central sphere represents the carbon atom while the oxygen atoms are modelled by the blue spheres):
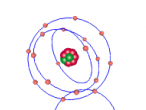
Carbon dioxide is a covalent molecule, consisting of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. These atoms join to form a double bong, with two electrons shared between each carbon and oxygen atoms, hence the structural formula: O=C=O. Carbon consists of 6 protons, 6 neutrons and 6 electrons distributed into two orbital shells; 2 in the initial shell and 4 in the second. The three naturally occurring isotopes of carbon are 12C, 13C and 14C. Oxygen contains a nucleus of 8 protons and 8 neutrons as well as 8 electrons. The electrons orbit around the nucleus in two shells; 2 in the first and 6 in the second.